Hydrogen Refueling Station Networks for Heavy-Duty Vehicles in Future Power Systems
A potential solution to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in the transport sector is to use alternatively fueled vehicles (AFV). Heavy-duty vehicles (HDV) emit a large share of GHG emissions in the transport sector and are therefore the subject of growing attention from global regulators. Fuel cell and green hydrogen technologies are a promising option to decarbonize HDVs, as their fast refueling and long vehicle ranges are in line with current logistic operation concepts. Moreover, the application of green hydrogen in transport could enable more effective integration of renewable energies (RE) across different energy sectors.
This paper explores the interplay between HDV Hydrogen Refueling Stations (HRS) that produce hydrogen locally and the power system by combining an infrastructure location planning model and an energy system optimization model that takes grid expansion options into account.
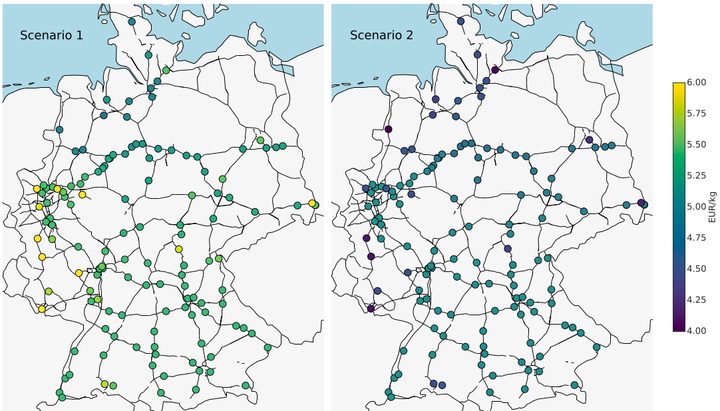
Two scenarios - one sizing refueling stations in symbiosis with the power system and one sizing them independently of it - are assessed regarding their impacts on the total annual energy system costs, regional RE integration and the levelized cost of hydrogen (LCOH). The impacts are calculated based on locational marginal pricing for 2050.
Depending on the integration scenario, we find average LCOH of between 5.66 euro/kg and 6.20 euro/kg, for which nodal electricity prices are the main determining factor as well as a strong difference in LCOH between north and south Germany. From a system perspective, investing in HDV-HRS in symbiosis with the power system rather than independently promises cost savings of around one billion-euros per annum.
We therefore conclude that the co-optimization of multiple energy sectors is important for investment planning and has the potential to exploit synergies. or a policy-relevant case study of the German transmission system in terms of their speed-up in computation time, deviation from optimal total system cost, and similarity of line expansion.